Bitcoin – Technical Features
Posted On June 24, 2022
" A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they'll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone" Satoshi Nakamoto
Below are some slides referenced from a lecture hosted by Gary Gensler on 'Blockchain and Money'. In these lectures he breakes down the technical features of Bitcoin (a digital permissionless decentralized exchange network). He decomposes these features into three main categories listed below. For curious minds, his lectures are a gold mine. Enjoy!
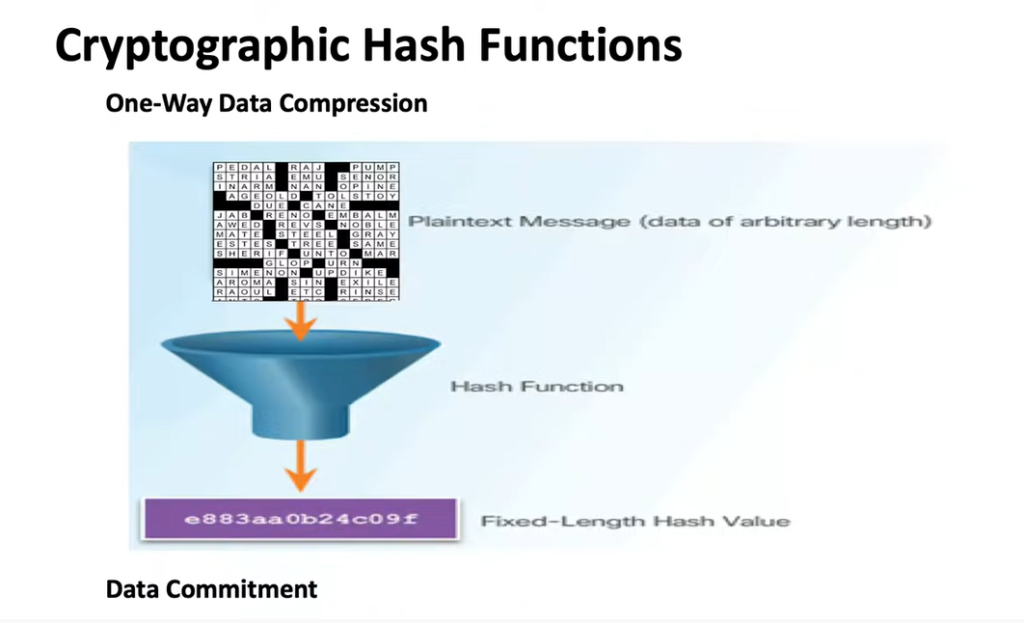
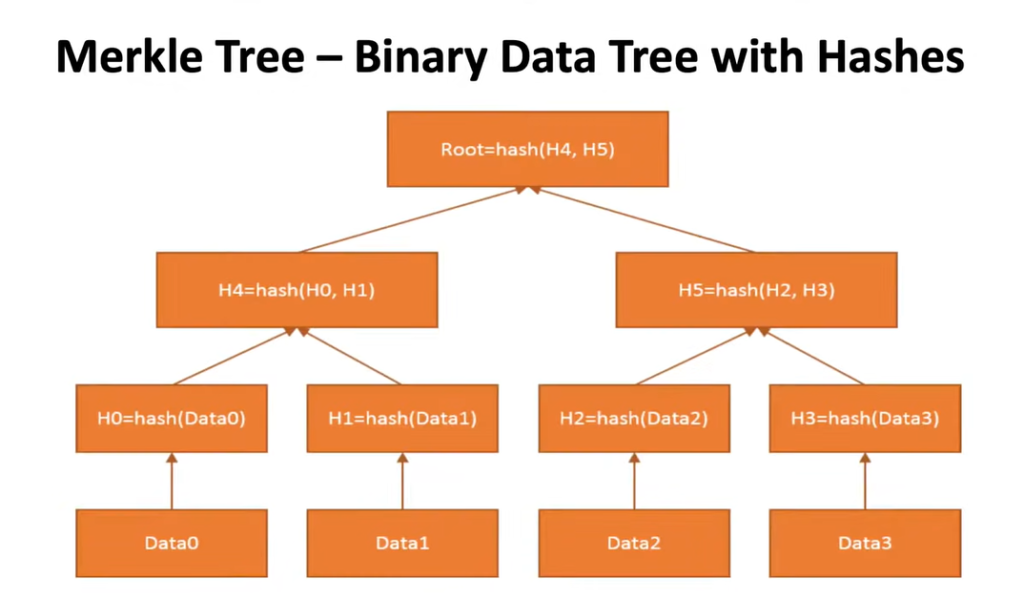
- Cryptography & Timestamped Logs
- Cryptographic Hash Functions
- Timestamped Append-only Logs (Blocks)
- Block Headers & Merkle Trees
- Asymmetric Cryptography & Digital Signatures
- Addresses
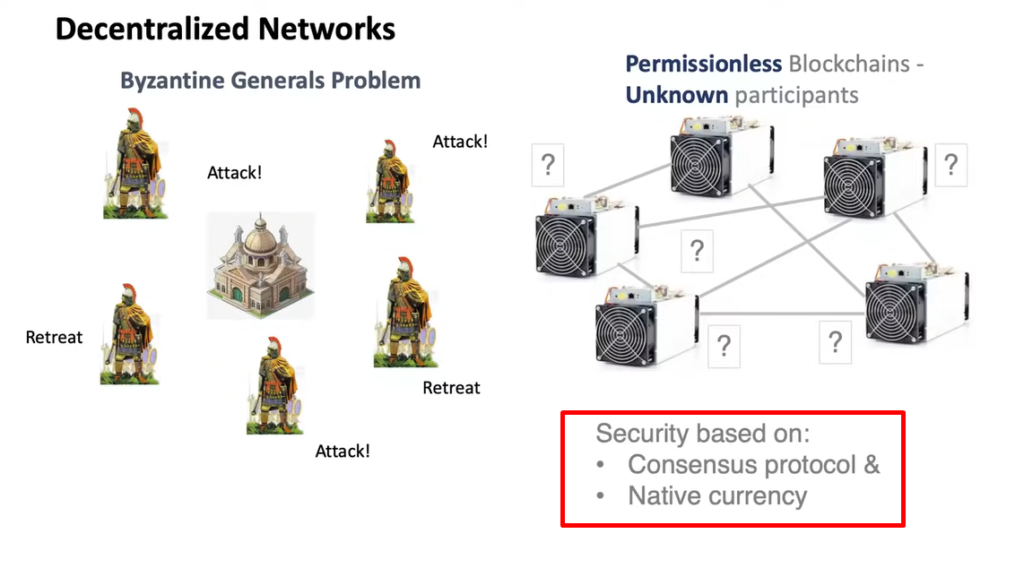
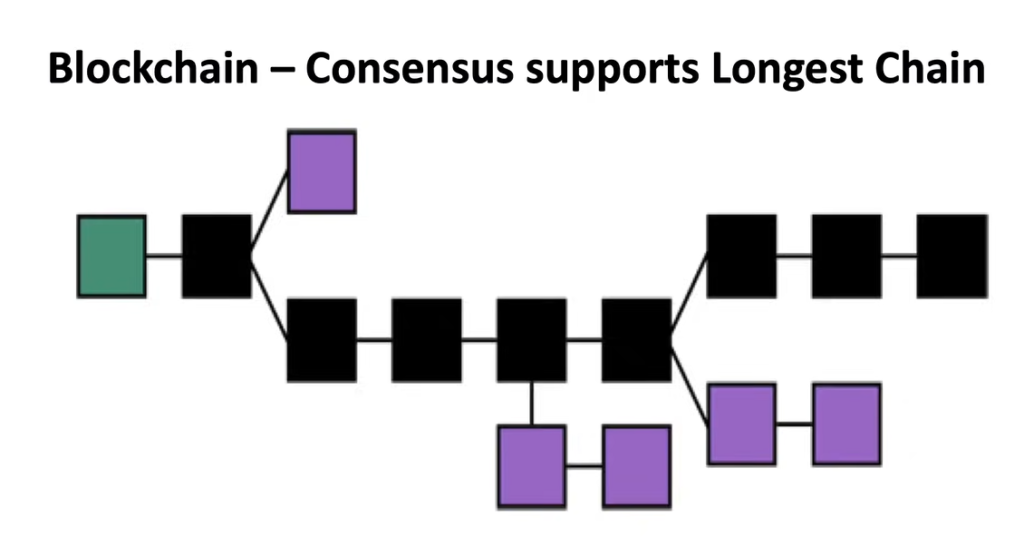
- Decentralized Network Consensus
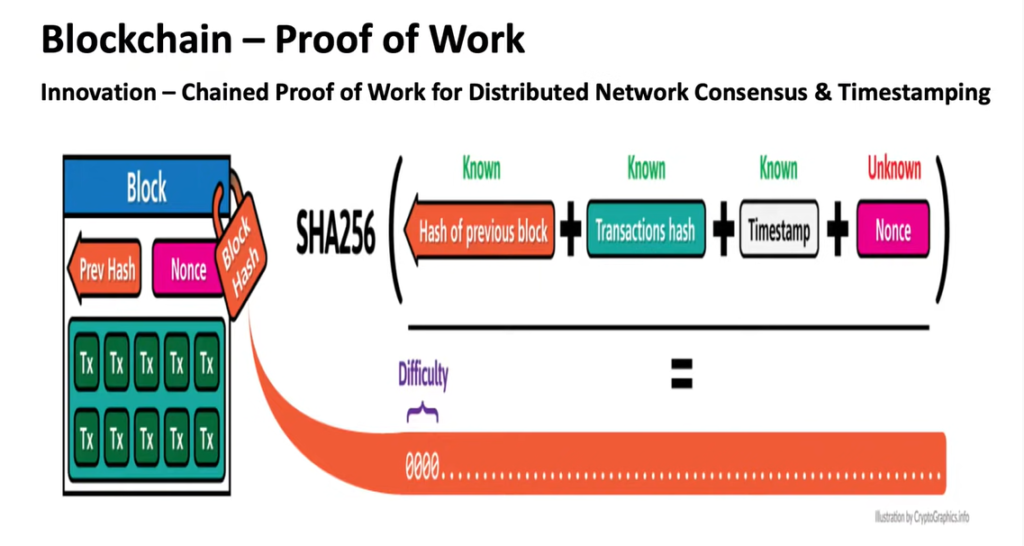
- Proof of Work
- Native Currency
- Network
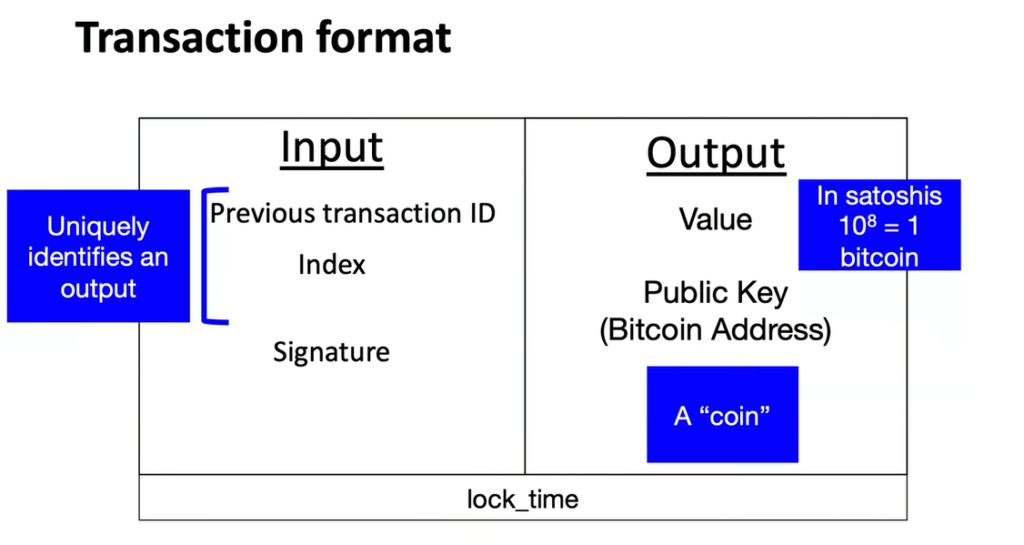
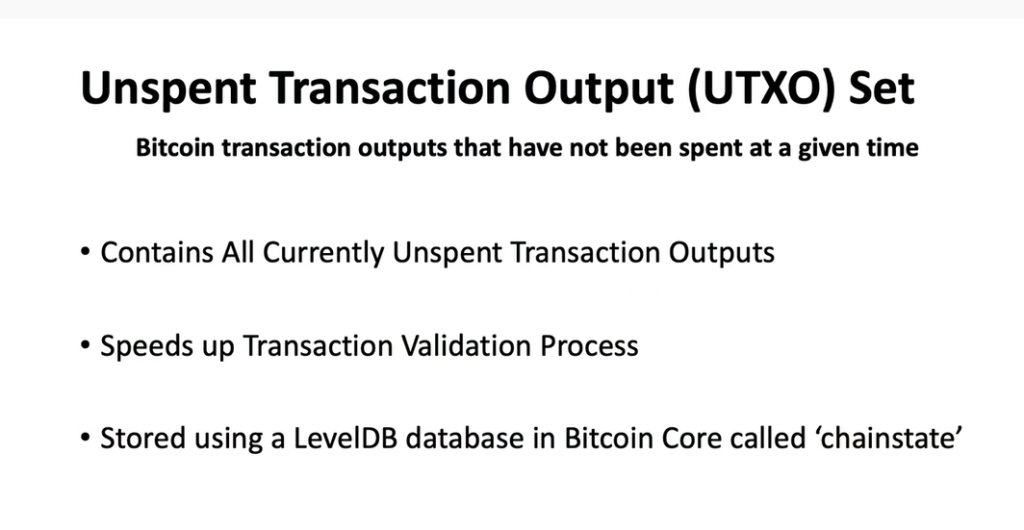
- Transaction Script & UTXO
- Transaction Inputs & Outputs
- Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) set
- Scripting language
Cryptography & Timestamped Logs

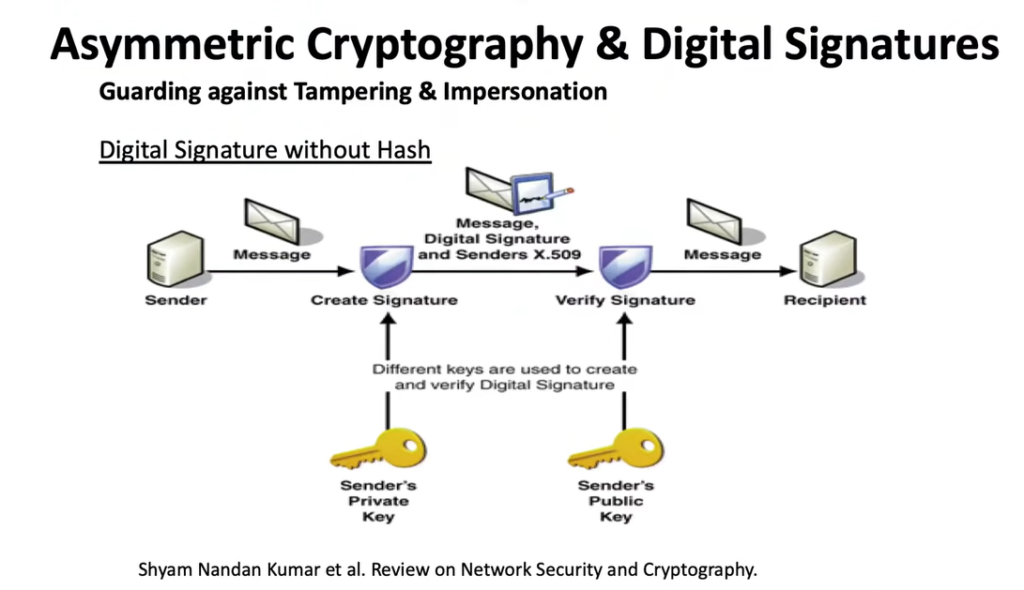
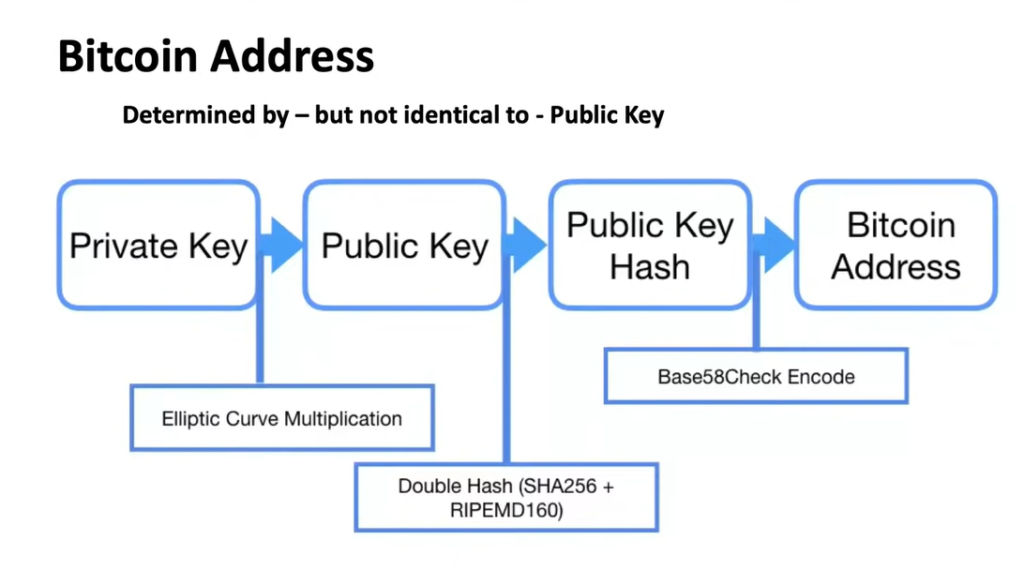
Decentralized Network Consensus


Transaction Script & UTXO